From the Metropolitan Museum website:
"Images of nature have remained a potent source of inspiration for artists down to the present day. While the Chinese landscape has been transformed by millennia of human occupation, Chinese artistic expression has also been deeply imprinted with images of the natural world. Viewing Chinese landscape paintings, it is clear that Chinese depictions of nature are seldom mere representations of the external world. Rather, they are expressions of the mind and heart of the individual artists—cultivated landscapes that embody the culture and cultivation of their masters."
http://www.metmuseum.org/toah/hd/clpg/hd_clpg.htm
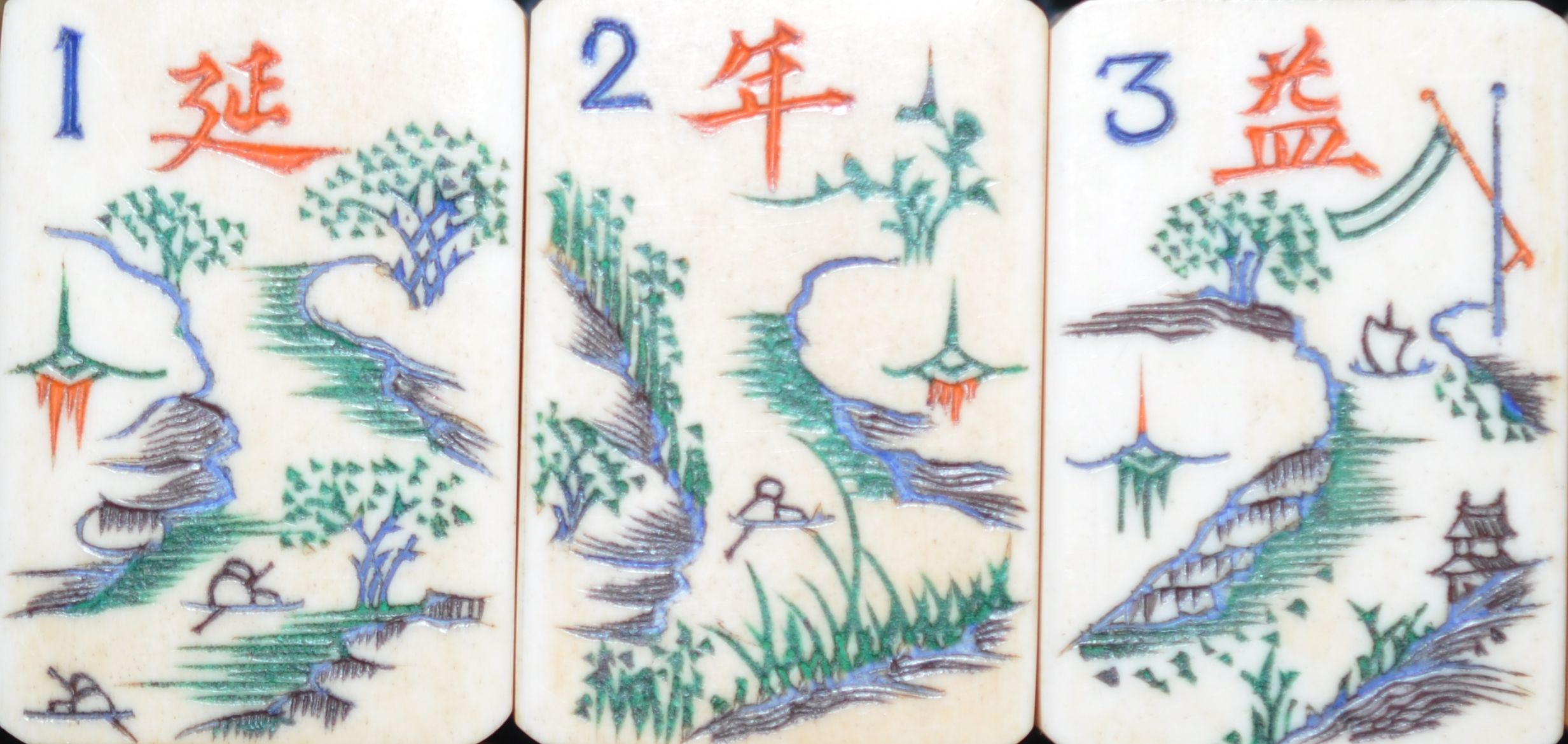

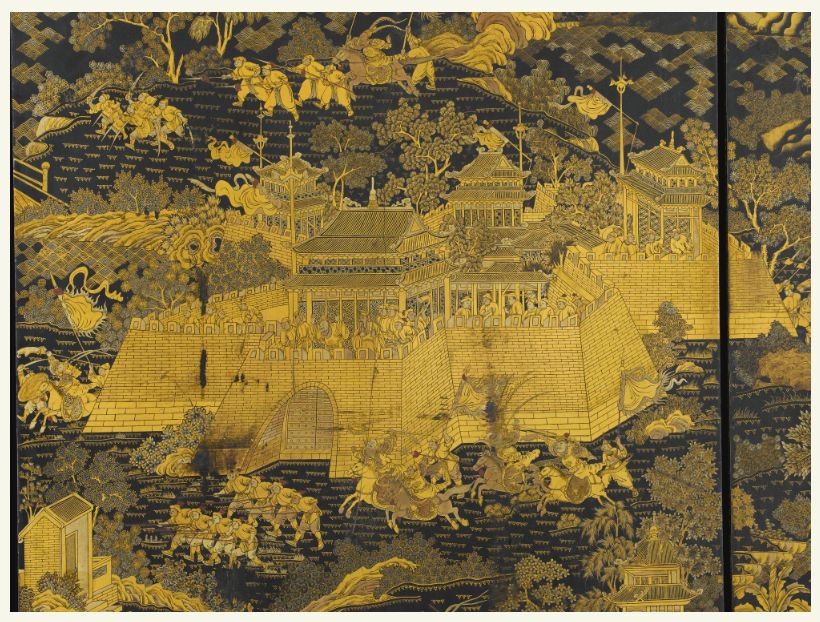
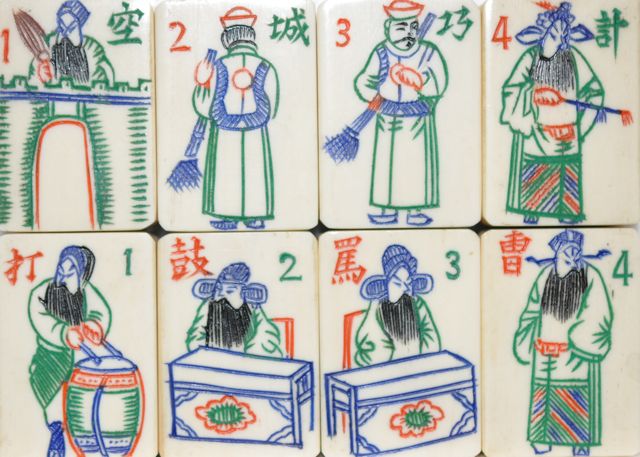
The artist who carved these bone and ebony tiles created designs similar to those done by other Chinese artists who worked in other media such as watercolors and ink drawing. Objects were captured with a few strokes giving the viewer all necessary clues to know what was depicted.
Here are two works from the Metropolitan Museum of Art:

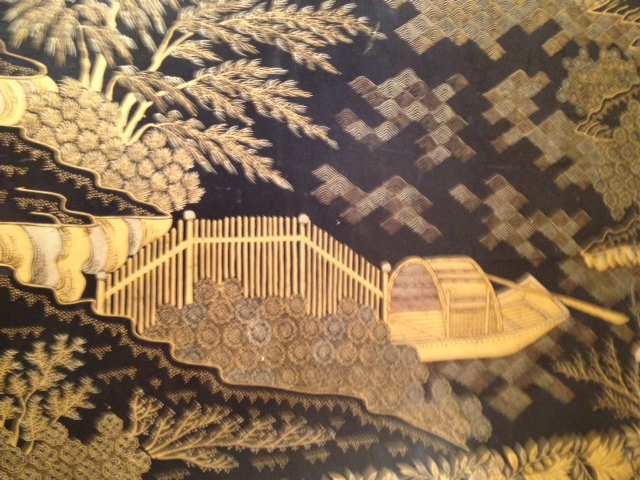
The artist has captured the essence of the scene, with a fisherman in a boat halfway up on the left, and two bridges, one in the forefront and one in the center.
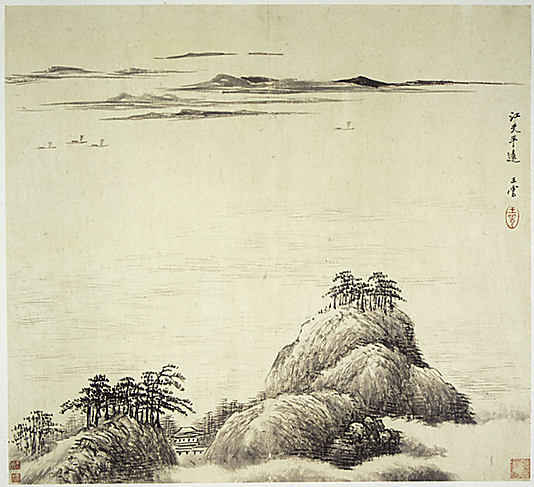

This beautiful work features sailboats in the distance. The boats in each help to fill the void created by the water, fitting in with Chinese design principles.
This from the Metropolitan Museum website describing these works:
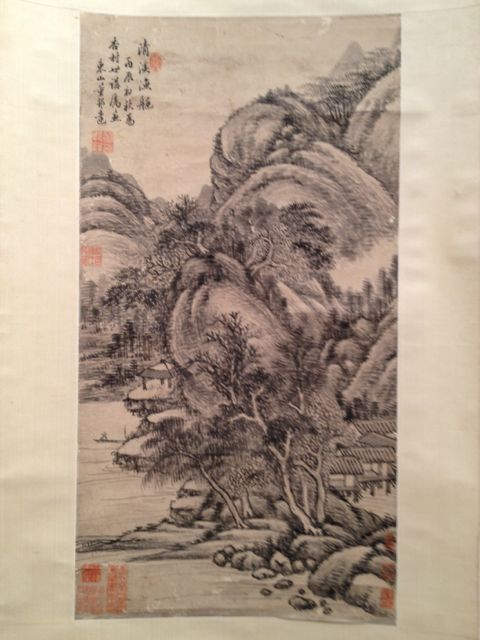
"In 1691 Wang Hui, the leading artist of his day, was summoned to Beijing to oversee the creation of a mammoth imperial commission documenting the Kangxi emperor's southern inspection tour of 1689. The painting, consisting of twelve monumental handscrolls, is the largest pictorial work of the Qing dynasty. (The Metropolitan owns one scroll from this set; acc. no. 1979.5.) Since the finished set bears no artists' signatures or seals, it is only through group works such as the Museum's new acquisition that the identity of Wang's artistic team can be established. The album, in which four younger artists from Wang's home region practiced the methods of ancient artists, is a rare example of a master painter's having recruited assistants and shaped their style to conform to the orthodox manner, which epitomized scholarly taste at that time. This academic style became the hallmark of all later Qing court commissions.
The leaf illustrated here, Mountain Waterfall, is by Wang Hui's leading disciple, Yang Jin, who has inscribed it with a poem:
For ten days spring clouds have obscured the stream's source;
In the middle of the night a west wind brings rain to the [mountain's] foot.
But I feel the urgent thunder roar in the empty valley,
So from a distance I know that the myriad gorges are competing in their flows."
Anyone else notice the artist wrote a poem on the painting? It is just like the carvers who added poems and sayings on many of our Mahjong tiles!
This paraphrase from the Ink Dance Chinese Paintings's website helps to explain the reliance on boats in waterscape scenes:
When painting a landscape scene featuring water, a mountain is the face, buildings on ridges are the eyes and a fisherman in a boat is the soul. Water becomes charming when it embellishes a mountain; it becomes clear when it has buildings near it; it shows greater perspective when there are boats.
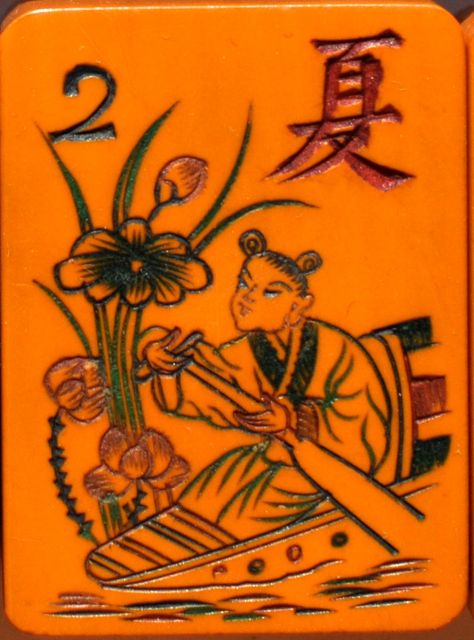
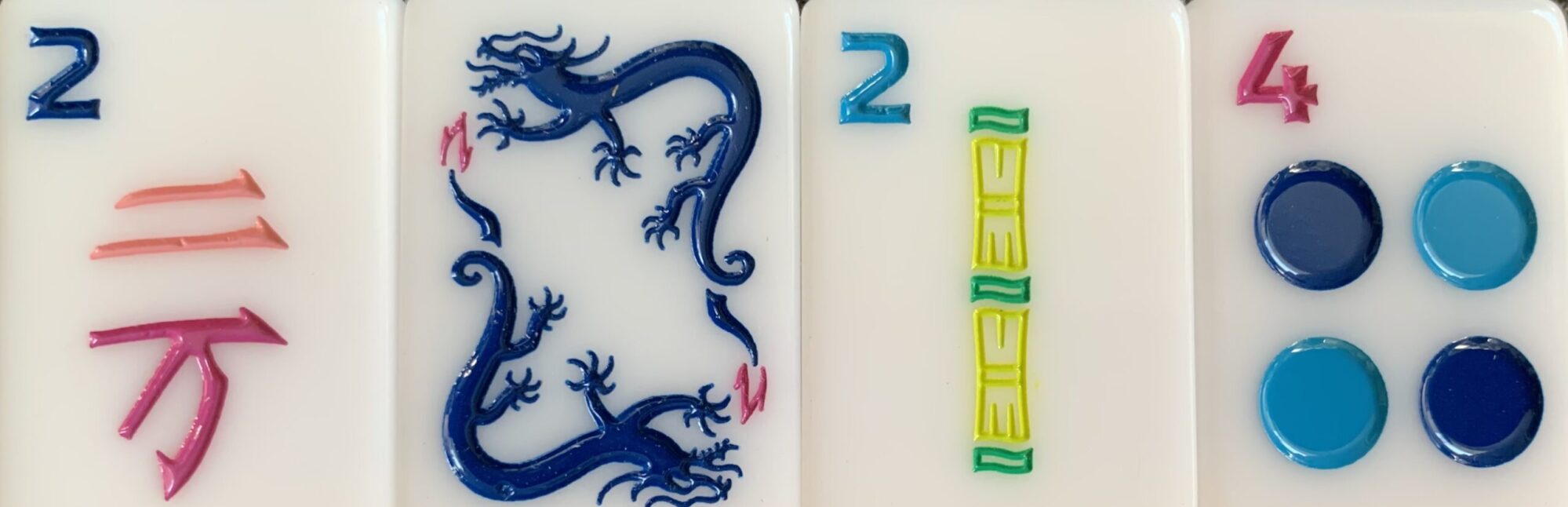
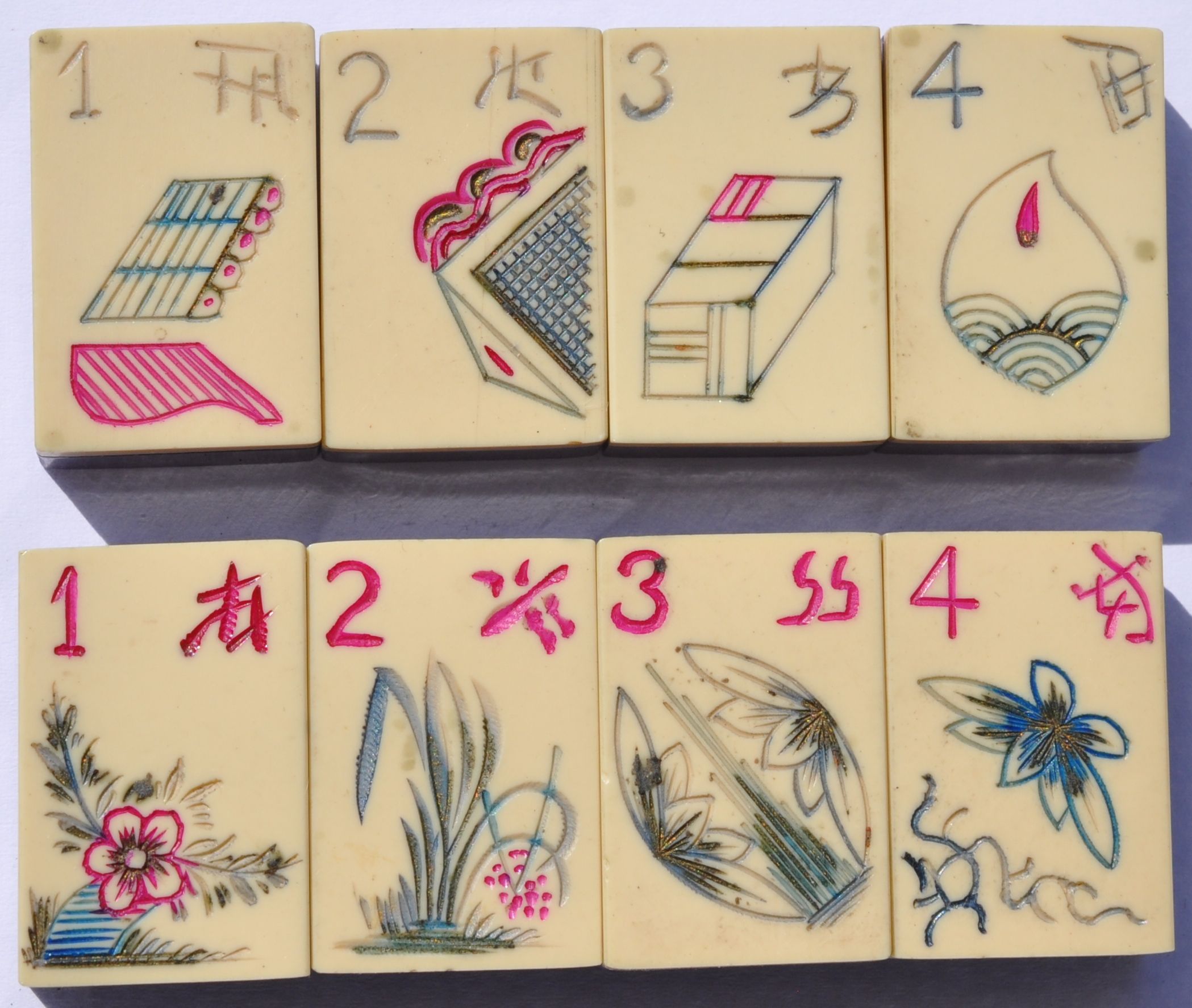
Following are examples of some boats on Mahjong tiles.

You can see different boats on these tiles, a sailboat and some small fishing boats.

A sailboat from The Pung Chow Company
And a small Chinese Bakelite boat